Calculation of Molar Volume and Density at Fixed Temperature
Purpose: Learn to calculate physical properties in a system
Module: PanPhaseDiagram
Thermodynamic and molar volume Database: AlMg_MV.tdb
Batch file: Example_#1.12.pbfx
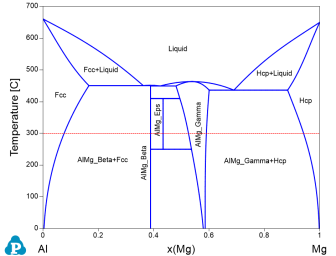
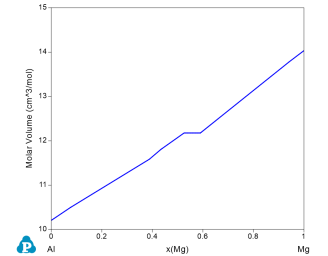
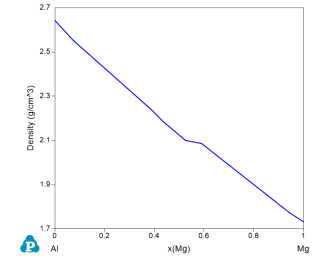
Figure 1 is the Al-Mg binary phase diagram. In this example, we learn to calculate the molar volume and density of the system as a function of x(Mg) at 300°C (the red dash line).
Calculation Method 1, From menu bar “Property”:
-
Load AlMg_MV.tdb following the procedure in Pandat User's Guide: Load Database , and select Al and Mg two components;
-
Click “Property” on the menu bar and select “Physical Property”;
-
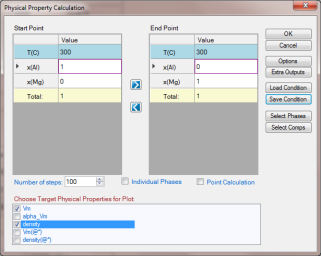
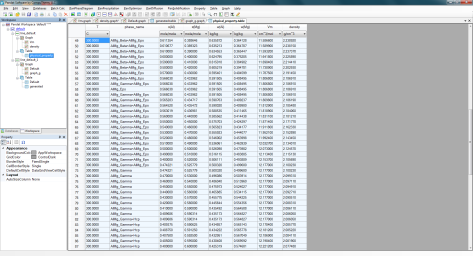
Set Calculation Condition as shown in Figure 2. The property selected is Vm (molar volume) and density;
Calculation Method 2, From menu bar “PanPhaseDiagram”:
-
Load AlMg_MV.tdb following the procedure in Pandat User's Guide: Load Database, and select Al and Mg two components;
-
Click “PanPhaseDiagram” on the menu bar and select “Line Calculation”;
-
Add the new table following the procedure in Pandat User's Guide: Icons for Table on Toolbar , and select Table Type as "Physical_Property"